이진 탐색 트리 (Binary Search Tree, BST)
각 노드가 최대 두 개의 자식 노드를 가지며, 각 노드의 왼쪽 서브 트리는 해당 노드보다 작은 값들로, 오른쪽 서브 트리는 해당 노드보다 큰 값들로 이루어진 자료구조이다.
이렇게 구성된 트리는 탐색 및 삽입 연산이 빠르게 수행된다.
🔗 Binary Tree 3가지 순회방법
🔗 BST insertion/deletion
이진 탐색 트리 특징
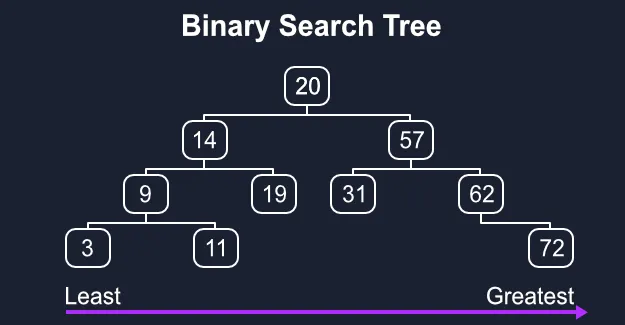
- 정렬된 구조: 모든 노드는 왼쪽 자식 < 부모 < 오른쪽 자식 규칙을 따른다.
이 덕분에 데이터가 자연스럽게 정렬된 상태를 유지한다. - 범위 시각화: 이미지 하단의 화살표처럼, 가장 왼쪽에 있는 노드가 최솟값(Least), 가장 오른쪽에 있는 노드가 최댓값(Greatest)이 된다.
- 효율적인 탐색: 균형이 잘 잡힌 트리의 경우, 모든 연산(탐색, 삽입, 삭제)의 시간 복잡도는 트리의 높이에 비례하는 O(log n)이다.
시간 복잡도
| 연산 | 평균 | 최악 (편향 트리) |
|---|---|---|
| 탐색 (Search) | O(log n) | O(n) |
| 삽입 (Insert) | O(log n) | O(n) |
| 삭제 (Delete) | O(log n) | O(n) |
트리가 한쪽으로 치우친 편향 트리(Skewed Tree)가 되면 연결 리스트와 다를 바 없어 O(n)이 된다.
이를 방지하기 위해 AVL 트리, Red-Black 트리 등 균형 트리를 사용한다.
주요 연산
탐색 (Search)
루트에서 시작하여, 찾고자 하는 값이 현재 노드보다 작으면 왼쪽, 크면 오른쪽으로 이동한다.
javascript
function search(node, target) {
if (target === node.value) {
return node;
} else if (target < node.value) {
return search(node.left, target);
} else {
return search(node.right, target);
}
}삽입 (Insert)
탐색과 동일한 방식으로 내려가다가, 빈 자리(null)를 만나면 새 노드를 삽입한다.
javascript
function insert(node, value) {
if (node === null) {
return new Node(value);
}
if (value < node.value) {
node.left = insert(node.left, value);
} else if (value > node.value) {
node.right = insert(node.right, value);
}
// 중복 값은 무시
return node;
}삭제 (Delete)
삭제는 3가지 케이스로 나뉜다.
- 자식이 없는 노드: 그냥 삭제
- 자식이 하나인 노드: 자식을 현재 위치로 올림
- 자식이 둘인 노드: 오른쪽 서브트리의 최솟값(또는 왼쪽 서브트리의 최댓값)으로 대체
javascript
function deleteNode(node, target) {
if (node === null) return null;
if (target < node.value) {
node.left = deleteNode(node.left, target);
} else if (target > node.value) {
node.right = deleteNode(node.right, target);
} else {
// 삭제할 노드를 찾음
// Case 1 & 2: 자식이 없거나 하나인 경우
if (node.left === null) return node.right;
if (node.right === null) return node.left;
// Case 3: 자식이 둘인 경우
// 오른쪽 서브트리에서 최솟값을 찾아 대체
let minNode = node.right;
while (minNode.left !== null) {
minNode = minNode.left;
}
node.value = minNode.value;
node.right = deleteNode(node.right, minNode.value);
}
return node;
}자바스크립트로 BST 구현하기
javascript
class Node {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
class BinarySearchTree {
constructor() {
this.root = null;
}
// 삽입
insert(value) {
const newNode = new Node(value);
if (this.root === null) {
this.root = newNode;
return this;
}
let current = this.root;
while (true) {
if (value === current.value) return this; // 중복 무시
if (value < current.value) {
if (current.left === null) {
current.left = newNode;
return this;
}
current = current.left;
} else {
if (current.right === null) {
current.right = newNode;
return this;
}
current = current.right;
}
}
}
// 탐색
search(value) {
let current = this.root;
while (current !== null) {
if (value === current.value) return current;
if (value < current.value) {
current = current.left;
} else {
current = current.right;
}
}
return null;
}
// 중위 순회 (정렬된 순서로 출력)
inOrderTraversal(node = this.root, result = []) {
if (node !== null) {
this.inOrderTraversal(node.left, result);
result.push(node.value);
this.inOrderTraversal(node.right, result);
}
return result;
}
// 최솟값
findMin(node = this.root) {
while (node.left !== null) {
node = node.left;
}
return node.value;
}
// 최댓값
findMax(node = this.root) {
while (node.right !== null) {
node = node.right;
}
return node.value;
}
}
const bst = new BinarySearchTree();
bst.insert(10);
bst.insert(5);
bst.insert(15);
bst.insert(3);
bst.insert(7);
console.log(bst.inOrderTraversal()); // [3, 5, 7, 10, 15]
console.log(bst.search(7)); // Node { value: 7, ... }
console.log(bst.findMin()); // 3
console.log(bst.findMax()); // 15